Chartered Companies
Chartered Companies are part of the factors responsible for the colonization of the African continent. These Companies played significant roles for their countries even before the Berlin conference of 1884 – 1885. It can be said that these chartered companies lay the foundation for the European countries in taking full control of African territories.
These chartered companies also stood as transnational actors in the European conquest of African society. The political, and socio-economic openings created by these chartered companies made it easy for the Europeans to avoid conflict between themselves during the scramble for the African countries.
According to A.G Hoppins, most of these charted companies started off as “merchant adventures” capitalists who lunch risky initiatives with limited capital and gradually move to play a significant role in the partition of Africa with powers given to them.”
How the chartered companies became powerful
These Companies became powerful most especially after they were granted Charters by Imperial leaders of European Countries. The power given to them by the imperial leaders made these chartered companies play more than a commercial role but also a political role in Africa.
For Instance, the British granted their chartered companies the Royal Charter. The Royal Charter is a formal grant given by the British Monarch to the chartered companies to make laws and sign treaties.
The German Chartered Companies were also given granted similar power by the German Kaiser. The charter was called Imperial Protection.
List of Some Chartered Companies in Colonial Africa
- United African Company (1882)
- National African Company (1884)
- Royal Niger Company (1886) (The United African Company was changed to the National African Company and then Royal Niger Company attributed to George Taubman Goldie.
- British South African Company (BSAC) was attributed to Cecil Rhodes when he acquired the Royal Charter in 1889.
- Imperial British East Africa Company
- The British-India Steam Navigation Company
- Portuguese Guinea Company
- Royal African Company
- British South African company
Initial Roles of the Chartered Companies
- The Initial role of the Chartered Companies in Africa at first was basically trading, as the majority of the Chartered Companies were controlled by merchants and Sailors. For instance, Adolf Woermann was a German merchant who played significant roles in West Africa to the extent he was considered the largest German trader in the area.
- Another role performed by these Chartered Companies before they were granted the Charter for political and socio-economic roles was buying and selling of Slaves.
The New Roles of Chartered Companies
The new roles of the chartered companies in Africa started from the moment there were granted Charters by their countries.
According to David Thomson, “Expansion into Africa was unbridled. in 1885 the African association converted itself into the Congo free state with Leopold II as its absolute sovereign. The success prompted other European powers to set up Companies to develop other African states, such Companies granted government monopoly rights in the exploitation of various territories and became the general media of colonial; commerce and appropriation in the subsequent decade”.
The companies began to play significant roles in the occupation of the African territories by signing treaties with the African kings and leaders. The signing of treaties with the African local chiefs gave the chartered companies the opportunity of creating a gradual colonial empire for their Country. For instance, the Royal Niger Company after being granted the royal charter in 1886, became a company that played a strong factor that led to southern Nigeria being controlled by the British.
The Effective roles played by these chartered companies gave the European countries the idea of the type of colonial system that could be used to control the areas. For instance, the British were able to understand the ideal administration that will be suitable in areas where treaties were signed through their Chartered companies. This is one of the reasons why the British practice indirect rule, the French used direct rule while the German used both direct and indirect rule based on areas.
ALSO
The Chartered Companies through the charter powers given to them by their different countries were able to set up commercial regulations and navigation rules in coastal areas that they controlled. This led to the monopolization of trade. for instance, the Royal Niger Company was able to break off any form of competition around the “Oil rivers” in the Niger area.
The ability of these companies to trade effectively gave more power to their countries to declare these areas as theirs during and after the Berlin Conference led by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck and French Jules Ferry the primmer of France.
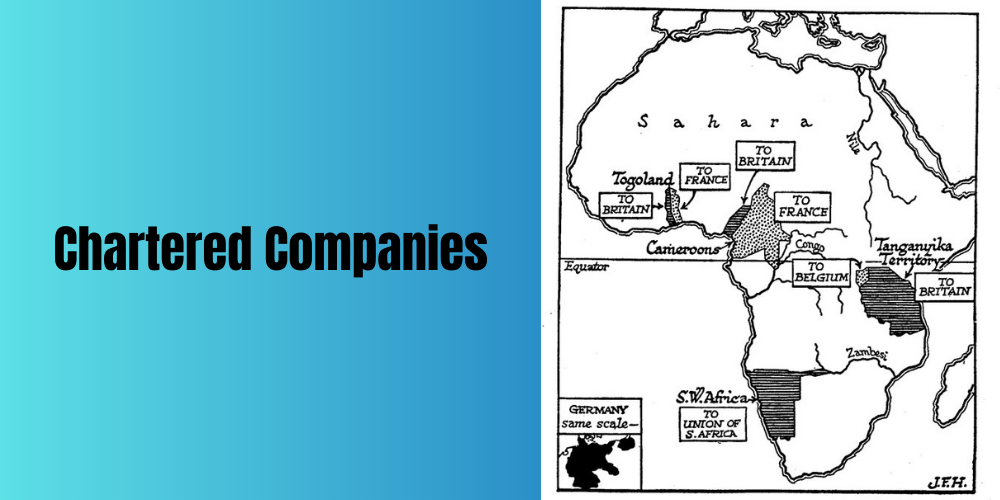
The Imperial British East Africa Company also helped the British secure modern-day Kenya and Uganda. While Cecil Rhodes also use the British South Africa Company to secure Rhodesia( both the northern and the southern Rhodesia) for the British. King Leopold ll of Belgium also use the chartered companies to secure Belgium’s positions in the Congo.
The German merchants also secure Tanganyika, Tanzania(German East Africa) Togo and Cameroon. Although Tanganyika and Togo were later invaded by the British and France during the first world war making Germany lose its hold on them.
Also, some of the territories that were forcefully overthrown by the Europeans were placed under the control of the British. These companies were also used by various European countries especially the French and the British to administer the territories that were acquired. This idea also helped the European countries with the opportunity of not to spend their resources on the cost of administration.
According to D.A.Low “The classic British policy for the scramble for Africa had been to carve out by diplomacy a sphere of influence and then authorize a chartered company to take up the burden, thus relieving the British taxpayers of the cost”
Results on African
It’s important to note that the majority of the chartered companies were granted charters in order to be used as a piece of administrative machinery in acquiring more territories. These decisions made by the imperial leaders of the European countries had several effects on Africans. The effects that are discussed are not the “effect of colonialism” but the effects of the roles played by the chartered companies before different European countries took over from them.
- The chartered companies aided the European rapid exploitation of African natural resources and human resources with their abilities to monopolize trade in their area of jurisdiction gave them these enormous strengths.
- Many of the border dispute in Africa after the end of colonization was a result of the clash of treaties signed by the charter companies. Also, some of these companies are transformed into modern multinational companies that still control some trades in Africa.
- These companies also aided the dethronement of several African leaders before the full control of their countries. For instance, before the British fully took over the areas controlled by the royal niger company in 1899. Nana of Iteskiri and Jaja of Opobo was sent off their throne.